7.2. Convolutions for Images¶ Open the notebook in SageMaker Studio Lab
Now that we understand how convolutional layers work in theory, we are ready to see how they work in practice. Building on our motivation of convolutional neural networks as efficient architectures for exploring structure in image data, we stick with images as our running example.
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
from mxnet import autograd, np, npx
from mxnet.gluon import nn
from d2l import mxnet as d2l
npx.set_np()
import jax
from flax import linen as nn
from jax import numpy as jnp
from d2l import jax as d2l
No GPU/TPU found, falling back to CPU. (Set TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=0 and rerun for more info.)
import tensorflow as tf
from d2l import tensorflow as d2l
7.2.1. The Cross-Correlation Operation¶
Recall that strictly speaking, convolutional layers are a misnomer, since the operations they express are more accurately described as cross-correlations. Based on our descriptions of convolutional layers in Section 7.1, in such a layer, an input tensor and a kernel tensor are combined to produce an output tensor through a cross-correlation operation.
Let’s ignore channels for now and see how this works with two-dimensional data and hidden representations. In Fig. 7.2.1, the input is a two-dimensional tensor with a height of 3 and width of 3. We mark the shape of the tensor as \(3 \times 3\) or (\(3\), \(3\)). The height and width of the kernel are both 2. The shape of the kernel window (or convolution window) is given by the height and width of the kernel (here it is \(2 \times 2\)).
Fig. 7.2.1 Two-dimensional cross-correlation operation. The shaded portions are the first output element as well as the input and kernel tensor elements used for the output computation: \(0\times0+1\times1+3\times2+4\times3=19\).¶
In the two-dimensional cross-correlation operation, we begin with the convolution window positioned at the upper-left corner of the input tensor and slide it across the input tensor, both from left to right and top to bottom. When the convolution window slides to a certain position, the input subtensor contained in that window and the kernel tensor are multiplied elementwise and the resulting tensor is summed up yielding a single scalar value. This result gives the value of the output tensor at the corresponding location. Here, the output tensor has a height of 2 and width of 2 and the four elements are derived from the two-dimensional cross-correlation operation:
Note that along each axis, the output size is slightly smaller than the input size. Because the kernel has width and height greater than \(1\), we can only properly compute the cross-correlation for locations where the kernel fits wholly within the image, the output size is given by the input size \(n_\textrm{h} \times n_\textrm{w}\) minus the size of the convolution kernel \(k_\textrm{h} \times k_\textrm{w}\) via
This is the case since we need enough space to “shift” the convolution
kernel across the image. Later we will see how to keep the size
unchanged by padding the image with zeros around its boundary so that
there is enough space to shift the kernel. Next, we implement this
process in the corr2d function, which accepts an input tensor X
and a kernel tensor K and returns an output tensor Y.
def corr2d(X, K): #@save
"""Compute 2D cross-correlation."""
h, w = K.shape
Y = torch.zeros((X.shape[0] - h + 1, X.shape[1] - w + 1))
for i in range(Y.shape[0]):
for j in range(Y.shape[1]):
Y[i, j] = (X[i:i + h, j:j + w] * K).sum()
return Y
def corr2d(X, K): #@save
"""Compute 2D cross-correlation."""
h, w = K.shape
Y = np.zeros((X.shape[0] - h + 1, X.shape[1] - w + 1))
for i in range(Y.shape[0]):
for j in range(Y.shape[1]):
Y[i, j] = (X[i:i + h, j:j + w] * K).sum()
return Y
def corr2d(X, K): #@save
"""Compute 2D cross-correlation."""
h, w = K.shape
Y = jnp.zeros((X.shape[0] - h + 1, X.shape[1] - w + 1))
for i in range(Y.shape[0]):
for j in range(Y.shape[1]):
Y = Y.at[i, j].set((X[i:i + h, j:j + w] * K).sum())
return Y
def corr2d(X, K): #@save
"""Compute 2D cross-correlation."""
h, w = K.shape
Y = tf.Variable(tf.zeros((X.shape[0] - h + 1, X.shape[1] - w + 1)))
for i in range(Y.shape[0]):
for j in range(Y.shape[1]):
Y[i, j].assign(tf.reduce_sum(
X[i: i + h, j: j + w] * K))
return Y
We can construct the input tensor X and the kernel tensor K from
Fig. 7.2.1 to validate the output of the above
implementation of the two-dimensional cross-correlation operation.
X = torch.tensor([[0.0, 1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0, 5.0], [6.0, 7.0, 8.0]])
K = torch.tensor([[0.0, 1.0], [2.0, 3.0]])
corr2d(X, K)
tensor([[19., 25.],
[37., 43.]])
X = np.array([[0.0, 1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0, 5.0], [6.0, 7.0, 8.0]])
K = np.array([[0.0, 1.0], [2.0, 3.0]])
corr2d(X, K)
[22:11:22] ../src/storage/storage.cc:196: Using Pooled (Naive) StorageManager for CPU
array([[19., 25.],
[37., 43.]])
X = jnp.array([[0.0, 1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0, 5.0], [6.0, 7.0, 8.0]])
K = jnp.array([[0.0, 1.0], [2.0, 3.0]])
corr2d(X, K)
Array([[19., 25.],
[37., 43.]], dtype=float32)
X = tf.constant([[0.0, 1.0, 2.0], [3.0, 4.0, 5.0], [6.0, 7.0, 8.0]])
K = tf.constant([[0.0, 1.0], [2.0, 3.0]])
corr2d(X, K)
<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(2, 2) dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[19., 25.],
[37., 43.]], dtype=float32)>
7.2.2. Convolutional Layers¶
A convolutional layer cross-correlates the input and kernel and adds a scalar bias to produce an output. The two parameters of a convolutional layer are the kernel and the scalar bias. When training models based on convolutional layers, we typically initialize the kernels randomly, just as we would with a fully connected layer.
We are now ready to implement a two-dimensional convolutional layer
based on the corr2d function defined above. In the __init__
constructor method, we declare weight and bias as the two model
parameters. The forward propagation method calls the corr2d function
and adds the bias.
class Conv2D(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, kernel_size):
super().__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.rand(kernel_size))
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1))
def forward(self, x):
return corr2d(x, self.weight) + self.bias
class Conv2D(nn.Block):
def __init__(self, kernel_size, **kwargs):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.weight = self.params.get('weight', shape=kernel_size)
self.bias = self.params.get('bias', shape=(1,))
def forward(self, x):
return corr2d(x, self.weight.data()) + self.bias.data()
class Conv2D(nn.Module):
kernel_size: int
def setup(self):
self.weight = nn.param('w', nn.initializers.uniform, self.kernel_size)
self.bias = nn.param('b', nn.initializers.zeros, 1)
def forward(self, x):
return corr2d(x, self.weight) + self.bias
class Conv2D(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def build(self, kernel_size):
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer()
self.weight = self.add_weight(name='w', shape=kernel_size,
initializer=initializer)
self.bias = self.add_weight(name='b', shape=(1, ),
initializer=initializer)
def call(self, inputs):
return corr2d(inputs, self.weight) + self.bias
In \(h \times w\) convolution or an \(h \times w\) convolution kernel, the height and width of the convolution kernel are \(h\) and \(w\), respectively. We also refer to a convolutional layer with an \(h \times w\) convolution kernel simply as an \(h \times w\) convolutional layer.
7.2.3. Object Edge Detection in Images¶
Let’s take a moment to parse a simple application of a convolutional layer: detecting the edge of an object in an image by finding the location of the pixel change. First, we construct an “image” of \(6\times 8\) pixels. The middle four columns are black (\(0\)) and the rest are white (\(1\)).
X = torch.ones((6, 8))
X[:, 2:6] = 0
X
tensor([[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.]])
X = np.ones((6, 8))
X[:, 2:6] = 0
X
array([[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.]])
X = jnp.ones((6, 8))
X = X.at[:, 2:6].set(0)
X
Array([[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.]], dtype=float32)
X = tf.Variable(tf.ones((6, 8)))
X[:, 2:6].assign(tf.zeros(X[:, 2:6].shape))
X
<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(6, 8) dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.]], dtype=float32)>
Next, we construct a kernel K with a height of 1 and a width of 2.
When we perform the cross-correlation operation with the input, if the
horizontally adjacent elements are the same, the output is 0. Otherwise,
the output is nonzero. Note that this kernel is a special case of a
finite difference operator. At location \((i,j)\) it computes
\(x_{i,j} - x_{(i+1),j}\), i.e., it computes the difference between
the values of horizontally adjacent pixels. This is a discrete
approximation of the first derivative in the horizontal direction. After
all, for a function \(f(i,j)\) its derivative
\(-\partial_i f(i,j) = \lim_{\epsilon \to 0} \frac{f(i,j) - f(i+\epsilon,j)}{\epsilon}\).
Let’s see how this works in practice.
K = torch.tensor([[1.0, -1.0]])
K = np.array([[1.0, -1.0]])
K = jnp.array([[1.0, -1.0]])
K = tf.constant([[1.0, -1.0]])
We are ready to perform the cross-correlation operation with arguments
X (our input) and K (our kernel). As you can see, we detect
\(1\) for the edge from white to black and \(-1\) for the edge
from black to white. All other outputs take value \(0\).
Y = corr2d(X, K)
Y
tensor([[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.]])
Y = corr2d(X, K)
Y
array([[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.]])
Y = corr2d(X, K)
Y
Array([[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.]], dtype=float32)
Y = corr2d(X, K)
Y
<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(6, 7) dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., -1., 0.]], dtype=float32)>
We can now apply the kernel to the transposed image. As expected, it
vanishes. The kernel K only detects vertical edges.
corr2d(X.t(), K)
tensor([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
corr2d(d2l.transpose(X), K)
array([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
corr2d(d2l.transpose(X), K)
Array([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]], dtype=float32)
corr2d(tf.transpose(X), K)
<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(8, 5) dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]], dtype=float32)>
7.2.4. Learning a Kernel¶
Designing an edge detector by finite differences [1, -1] is neat if
we know this is precisely what we are looking for. However, as we look
at larger kernels, and consider successive layers of convolutions, it
might be impossible to specify precisely what each filter should be
doing manually.
Now let’s see whether we can learn the kernel that generated Y from
X by looking at the input–output pairs only. We first construct a
convolutional layer and initialize its kernel as a random tensor. Next,
in each iteration, we will use the squared error to compare Y with
the output of the convolutional layer. We can then calculate the
gradient to update the kernel. For the sake of simplicity, in the
following we use the built-in class for two-dimensional convolutional
layers and ignore the bias.
# Construct a two-dimensional convolutional layer with 1 output channel and a
# kernel of shape (1, 2). For the sake of simplicity, we ignore the bias here
conv2d = nn.LazyConv2d(1, kernel_size=(1, 2), bias=False)
# The two-dimensional convolutional layer uses four-dimensional input and
# output in the format of (example, channel, height, width), where the batch
# size (number of examples in the batch) and the number of channels are both 1
X = X.reshape((1, 1, 6, 8))
Y = Y.reshape((1, 1, 6, 7))
lr = 3e-2 # Learning rate
for i in range(10):
Y_hat = conv2d(X)
l = (Y_hat - Y) ** 2
conv2d.zero_grad()
l.sum().backward()
# Update the kernel
conv2d.weight.data[:] -= lr * conv2d.weight.grad
if (i + 1) % 2 == 0:
print(f'epoch {i + 1}, loss {l.sum():.3f}')
epoch 2, loss 16.481
epoch 4, loss 5.069
epoch 6, loss 1.794
epoch 8, loss 0.688
epoch 10, loss 0.274
# Construct a two-dimensional convolutional layer with 1 output channel and a
# kernel of shape (1, 2). For the sake of simplicity, we ignore the bias here
conv2d = nn.Conv2D(1, kernel_size=(1, 2), use_bias=False)
conv2d.initialize()
# The two-dimensional convolutional layer uses four-dimensional input and
# output in the format of (example, channel, height, width), where the batch
# size (number of examples in the batch) and the number of channels are both 1
X = X.reshape(1, 1, 6, 8)
Y = Y.reshape(1, 1, 6, 7)
lr = 3e-2 # Learning rate
for i in range(10):
with autograd.record():
Y_hat = conv2d(X)
l = (Y_hat - Y) ** 2
l.backward()
# Update the kernel
conv2d.weight.data()[:] -= lr * conv2d.weight.grad()
if (i + 1) % 2 == 0:
print(f'epoch {i + 1}, loss {float(l.sum()):.3f}')
epoch 2, loss 4.949
epoch 4, loss 0.831
epoch 6, loss 0.140
epoch 8, loss 0.024
epoch 10, loss 0.004
[22:11:22] ../src/base.cc:48: GPU context requested, but no GPUs found.
# Construct a two-dimensional convolutional layer with 1 output channel and a
# kernel of shape (1, 2). For the sake of simplicity, we ignore the bias here
conv2d = nn.Conv(1, kernel_size=(1, 2), use_bias=False, padding='VALID')
# The two-dimensional convolutional layer uses four-dimensional input and
# output in the format of (example, height, width, channel), where the batch
# size (number of examples in the batch) and the number of channels are both 1
X = X.reshape((1, 6, 8, 1))
Y = Y.reshape((1, 6, 7, 1))
lr = 3e-2 # Learning rate
params = conv2d.init(jax.random.PRNGKey(d2l.get_seed()), X)
def loss(params, X, Y):
Y_hat = conv2d.apply(params, X)
return ((Y_hat - Y) ** 2).sum()
for i in range(10):
l, grads = jax.value_and_grad(loss)(params, X, Y)
# Update the kernel
params = jax.tree_map(lambda p, g: p - lr * g, params, grads)
if (i + 1) % 2 == 0:
print(f'epoch {i + 1}, loss {l:.3f}')
epoch 2, loss 23.292
epoch 4, loss 8.424
epoch 6, loss 3.263
epoch 8, loss 1.305
epoch 10, loss 0.529
# Construct a two-dimensional convolutional layer with 1 output channel and a
# kernel of shape (1, 2). For the sake of simplicity, we ignore the bias here
conv2d = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(1, (1, 2), use_bias=False)
# The two-dimensional convolutional layer uses four-dimensional input and
# output in the format of (example, height, width, channel), where the batch
# size (number of examples in the batch) and the number of channels are both 1
X = tf.reshape(X, (1, 6, 8, 1))
Y = tf.reshape(Y, (1, 6, 7, 1))
lr = 3e-2 # Learning rate
Y_hat = conv2d(X)
for i in range(10):
with tf.GradientTape(watch_accessed_variables=False) as g:
g.watch(conv2d.weights[0])
Y_hat = conv2d(X)
l = (abs(Y_hat - Y)) ** 2
# Update the kernel
update = tf.multiply(lr, g.gradient(l, conv2d.weights[0]))
weights = conv2d.get_weights()
weights[0] = conv2d.weights[0] - update
conv2d.set_weights(weights)
if (i + 1) % 2 == 0:
print(f'epoch {i + 1}, loss {tf.reduce_sum(l):.3f}')
epoch 2, loss 16.452
epoch 4, loss 3.301
epoch 6, loss 0.775
epoch 8, loss 0.221
epoch 10, loss 0.074
Note that the error has dropped to a small value after 10 iterations. Now we will take a look at the kernel tensor we learned.
conv2d.weight.data.reshape((1, 2))
tensor([[ 1.0398, -0.9328]])
conv2d.weight.data().reshape((1, 2))
array([[ 0.9895 , -0.9873705]])
params['params']['kernel'].reshape((1, 2))
Array([[ 1.0637044, -0.9139465]], dtype=float32)
tf.reshape(conv2d.get_weights()[0], (1, 2))
<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 2), dtype=float32, numpy=array([[ 1.0062983 , -0.95448595]], dtype=float32)>
Indeed, the learned kernel tensor is remarkably close to the kernel
tensor K we defined earlier.
7.2.5. Cross-Correlation and Convolution¶
Recall our observation from Section 7.1 of the correspondence between the cross-correlation and convolution operations. Here let’s continue to consider two-dimensional convolutional layers. What if such layers perform strict convolution operations as defined in (7.1.6) instead of cross-correlations? In order to obtain the output of the strict convolution operation, we only need to flip the two-dimensional kernel tensor both horizontally and vertically, and then perform the cross-correlation operation with the input tensor.
It is noteworthy that since kernels are learned from data in deep learning, the outputs of convolutional layers remain unaffected no matter such layers perform either the strict convolution operations or the cross-correlation operations.
To illustrate this, suppose that a convolutional layer performs cross-correlation and learns the kernel in Fig. 7.2.1, which is here denoted as the matrix \(\mathbf{K}\). Assuming that other conditions remain unchanged, when this layer instead performs strict convolution, the learned kernel \(\mathbf{K}'\) will be the same as \(\mathbf{K}\) after \(\mathbf{K}'\) is flipped both horizontally and vertically. That is to say, when the convolutional layer performs strict convolution for the input in Fig. 7.2.1 and \(\mathbf{K}'\), the same output in Fig. 7.2.1 (cross-correlation of the input and \(\mathbf{K}\)) will be obtained.
In keeping with standard terminology in deep learning literature, we will continue to refer to the cross-correlation operation as a convolution even though, strictly-speaking, it is slightly different. Furthermore, we use the term element to refer to an entry (or component) of any tensor representing a layer representation or a convolution kernel.
7.2.6. Feature Map and Receptive Field¶
As described in Section 7.1.4, the convolutional layer output in Fig. 7.2.1 is sometimes called a feature map, as it can be regarded as the learned representations (features) in the spatial dimensions (e.g., width and height) to the subsequent layer. In CNNs, for any element \(x\) of some layer, its receptive field refers to all the elements (from all the previous layers) that may affect the calculation of \(x\) during the forward propagation. Note that the receptive field may be larger than the actual size of the input.
Let’s continue to use Fig. 7.2.1 to explain the receptive field. Given the \(2 \times 2\) convolution kernel, the receptive field of the shaded output element (of value \(19\)) is the four elements in the shaded portion of the input. Now let’s denote the \(2 \times 2\) output as \(\mathbf{Y}\) and consider a deeper CNN with an additional \(2 \times 2\) convolutional layer that takes \(\mathbf{Y}\) as its input, outputting a single element \(z\). In this case, the receptive field of \(z\) on \(\mathbf{Y}\) includes all the four elements of \(\mathbf{Y}\), while the receptive field on the input includes all the nine input elements. Thus, when any element in a feature map needs a larger receptive field to detect input features over a broader area, we can build a deeper network.
Receptive fields derive their name from neurophysiology. A series of experiments on a range of animals using different stimuli (Hubel and Wiesel, 1959, Hubel and Wiesel, 1962, Hubel and Wiesel, 1968) explored the response of what is called the visual cortex on said stimuli. By and large they found that lower levels respond to edges and related shapes. Later on, Field (1987) illustrated this effect on natural images with, what can only be called, convolutional kernels. We reprint a key figure in Fig. 7.2.2 to illustrate the striking similarities.
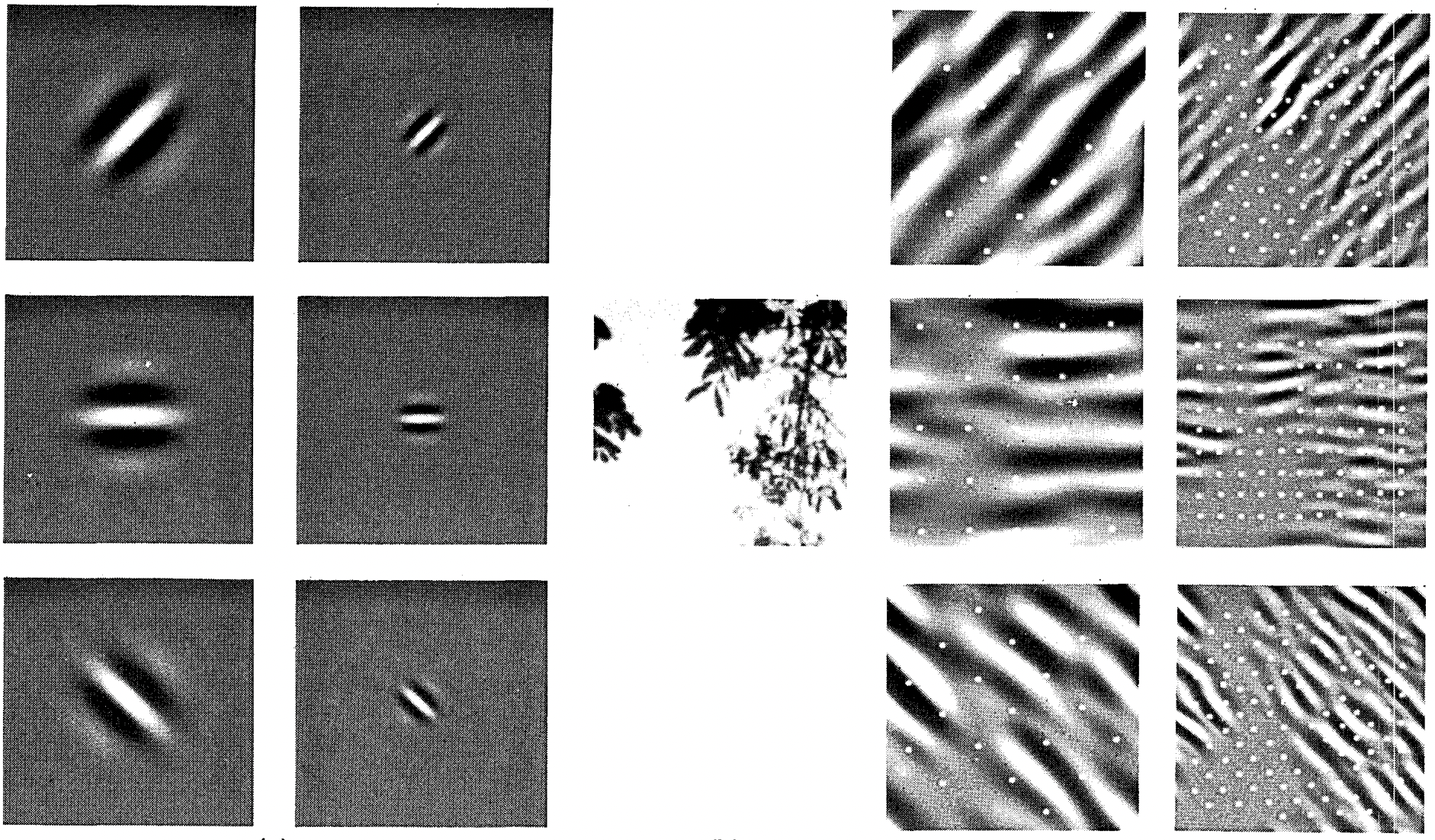
Fig. 7.2.2 Figure and caption taken from Field (1987): An example of coding with six different channels. (Left) Examples of the six types of sensor associated with each channel. (Right) Convolution of the image in (Middle) with the six sensors shown in (Left). The response of the individual sensors is determined by sampling these filtered images at a distance proportional to the size of the sensor (shown with dots). This diagram shows the response of only the even symmetric sensors.¶
As it turns out, this relation even holds for the features computed by deeper layers of networks trained on image classification tasks, as demonstrated in, for example, Kuzovkin et al. (2018). Suffice it to say, convolutions have proven to be an incredibly powerful tool for computer vision, both in biology and in code. As such, it is not surprising (in hindsight) that they heralded the recent success in deep learning.
7.2.7. Summary¶
The core computation required for a convolutional layer is a cross-correlation operation. We saw that a simple nested for-loop is all that is required to compute its value. If we have multiple input and multiple output channels, we are performing a matrix–matrix operation between channels. As can be seen, the computation is straightforward and, most importantly, highly local. This affords significant hardware optimization and many recent results in computer vision are only possible because of that. After all, it means that chip designers can invest in fast computation rather than memory when it comes to optimizing for convolutions. While this may not lead to optimal designs for other applications, it does open the door to ubiquitous and affordable computer vision.
In terms of convolutions themselves, they can be used for many purposes, for example detecting edges and lines, blurring images, or sharpening them. Most importantly, it is not necessary that the statistician (or engineer) invents suitable filters. Instead, we can simply learn them from data. This replaces feature engineering heuristics by evidence-based statistics. Lastly, and quite delightfully, these filters are not just advantageous for building deep networks but they also correspond to receptive fields and feature maps in the brain. This gives us confidence that we are on the right track.
7.2.8. Exercises¶
Construct an image
Xwith diagonal edges.What happens if you apply the kernel
Kin this section to it?What happens if you transpose
X?What happens if you transpose
K?
Design some kernels manually.
Given a directional vector \(\mathbf{v} = (v_1, v_2)\), derive an edge-detection kernel that detects edges orthogonal to \(\mathbf{v}\), i.e., edges in the direction \((v_2, -v_1)\).
Derive a finite difference operator for the second derivative. What is the minimum size of the convolutional kernel associated with it? Which structures in images respond most strongly to it?
How would you design a blur kernel? Why might you want to use such a kernel?
What is the minimum size of a kernel to obtain a derivative of order \(d\)?
When you try to automatically find the gradient for the
Conv2Dclass we created, what kind of error message do you see?How do you represent a cross-correlation operation as a matrix multiplication by changing the input and kernel tensors?
